Smart Cities and Smart Energy Industry
Actionable Strategies provides high value-add consultative services to attain breakthrough improvements when planning Smart Cities and Smart Grid initiatives. By applying both strategic business approaches and practical technical knowledge, we enable our clients to initiate, prove and execute projects on a journey to deploy advanced Smart City concepts and sophisticated Smart Grid technologies.
Our experience in industrialized countries has enabled us to help client in emerging markets. We combine the latest operational, information and communications technologies with proven practices from mature markets. Our recent successes in newly privatized markets where competition has just been introduced is a result of our work with customers, municipalities, utilities and regulators.
In an interview about driving strategic transformation, Actionable Strategies’ CEO discussed aligning metrics throughout the organization.
Strategy should be reflected in an overall metrics system that begins with outcomes, such as customer measures that reflect the output of a value chain.
In an example from the energy industry, he showed how strategic measures flowed down to operational measures and resulted in individual compensation metrics for employees.

Our consultative services are focused on the front half of the Smart Grid Lifecycle.
- Strategic business planning
- Architecture and roadmapping
- Engineering and IT integration
- Program management over project portfolios
We engage stakeholders across the value chain: suppliers, utilities, customers and regulators. Services start with the overall strategy and concept.
- Strategic planning to build a scalable and manageable Smart Grid busines model that incorporates customers, operations, regulators and financial stakeholders
- Architectural services to develop a pragmatic roadmap to extend existing technical investments, deploy the latest technologies and integrate operational and information technologies including seamless data interchange
- Engineering services to pragmatically design a grid that improves grid reliability and performance, while addressing variances in service territories, customer needs, communication capabilities and technology infrastructure
- Managed implementations to ensure pilots and early projects deliver demonstrable value in alignment with the strategic plan and architectural roadmap
Roles and Responsibilities
The most successful projects Actionable Strategies has delivered involved many contributors serving a diverse set of stakeholders. With Smart Grid projects, our strategic consultative capabilities articulate an achievable sequence of measurable goals. When translated into action plans, a number of defined projects are developed and managed as a portfolio supported by our expertise.
Program management of Smart Grid initiatives requires collaboration with a number of parties. In addition to resources drawn from the client, expertise and capacity must be provided by partners. These partners ensure early projects are successful and client leaders and staff gain the requisite knowledge required to assume ownership of Smart Grid operations and technology.
Partners work with the client to manage construction and implementation projects from concept to service transition. Operations and Maintenance are initially assisted but must quickly become part of standardized operations. As the client develops internal capabilities, they are able to execute future construction projects without assistance.
Engagement Structure
Actionable Strategies collaborates with clients to plan the journey to an advanced Smart Grid that introduces change at a reasonable pace. Breakthrough gains are achievable by leveraging the capabilities of Actionable Strategies and partner firms who bring the expertise and experience from other successful Smart Grid implementations.
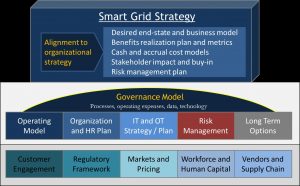 Adopting Smart Grid technologies can yield tremendous benefits across the energy value chain.
Adopting Smart Grid technologies can yield tremendous benefits across the energy value chain.
The potential for Smart Grid is attractive but realizing benefits is a significant challenge due to the higher velocity of the technology and operating models.
Successful implementation of a Smart Grid requires a solid strategic plan that results in a well-managed program for coordinated execution of projects. Actionable Strategies applies a proven framework to create the overall models and interlinked plans.
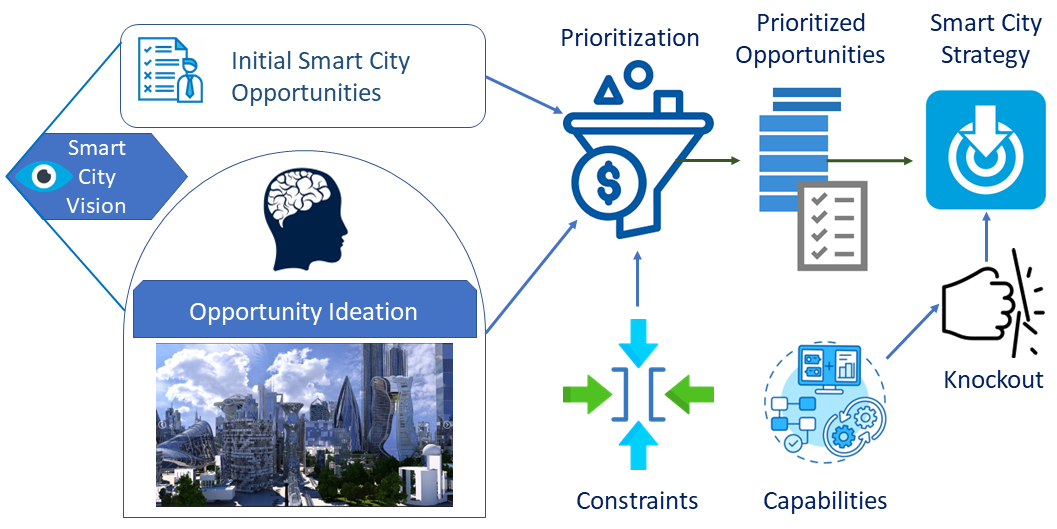
The concepts from Smart Cities are now more broadly applied to Smart Communities which include suburban and rural municipalities, campuses, distributed corporate locations, and managed real estate portfolios.
Component technologies have evolved and most deliver the promised benefits. The challenges are those faced by all complex initiatives that rely on many advanced technologies that integrate into existing organizations.
Our approach addresses these factors that can limit or inhibit success.
No Smart City initiative ever includes every possible domain. In fact, some of our clients are opposed to or prevented by regulation from implementing certain applications (e.g., video surveillance). Actionable Strategies has experience with the individual domains but most importantly, with integrating them and creating an overall governance structure with end-to-end processes.
The potential benefits of Smart City technologies extend to suburban and rural municipalities, campuses, distributed corporate locations, and managed real estate portfolios. The framework and approaches apply directly to each of these types of clients.
It is essential that none of the domains are considered in isolation. Rather, they should be treated as a component in providing a specific benefit to one or more stakeholders.
Smart Governance
Smart Mobility
Smart Energy
Smart Economy
Smart Buildings
Smart Environment
Smart Health
Smart Safety and Security
 Actionable Strategies created the strategy and technology roadmap for the Central Power Corporation of Vietnam. Rapid economic growth placed pressure on the power grid for all sectors of the economy. The adoption of free market reforms demanded a modern market structure with organizations able to make the transition to a market economy. The Central Power Corporation required a strategy and extended roadmap to enable it to operate effectively in a competitive structure.
Actionable Strategies created the strategy and technology roadmap for the Central Power Corporation of Vietnam. Rapid economic growth placed pressure on the power grid for all sectors of the economy. The adoption of free market reforms demanded a modern market structure with organizations able to make the transition to a market economy. The Central Power Corporation required a strategy and extended roadmap to enable it to operate effectively in a competitive structure.
The project had ambitious goals to make the utility world class across all facets of the company. Specific business goals were defined and assigned underlying target metrics.
- Reduce system losses
- Improve management
- Improve operational efficiency
- Improve the quality of supply and electricity services to customers
 Actionable Strategies evaluated the potential for a variety of Smart City technologies for the campus of the University Politehnica of Bucharest, the largest and oldest technical university in Romania. The technical, financial, regulatory and environmental feasibility were assessed.
Actionable Strategies evaluated the potential for a variety of Smart City technologies for the campus of the University Politehnica of Bucharest, the largest and oldest technical university in Romania. The technical, financial, regulatory and environmental feasibility were assessed.
The study ultimately led to funding for the Smart Campus initiative.
- Smart Grid and Microgrids
- Smart Lighting
- Solar Power
- Electric Vehicles
- Smart Buildings
- Smart Transportation
The Smart Grid included Distributed Energy Resources and energy storage.
 Actionable Strategies created the strategy for a Smart Grid in Myanmar. Initially focused in the capital, Yangon, a roadmap was developed which progressed from grid modernization to support for Smart Cities in Myanmar. The Smart Grid roadmap led to a proposal for project financing requiring approval from diverse stakeholders including state owned transmission and distribution companies. Ultimately, the Ministry of Electricity and Energy approved the strategic plan that included quantified benefits, risks, and financial projections.
Actionable Strategies created the strategy for a Smart Grid in Myanmar. Initially focused in the capital, Yangon, a roadmap was developed which progressed from grid modernization to support for Smart Cities in Myanmar. The Smart Grid roadmap led to a proposal for project financing requiring approval from diverse stakeholders including state owned transmission and distribution companies. Ultimately, the Ministry of Electricity and Energy approved the strategic plan that included quantified benefits, risks, and financial projections.
Initial implementation in 10 townships of $200 million was secured. Additional debt financing of $500 million was arranged for subsequent expansion. Unfortunately, the Coup d’État occurred two days before the Minister could formally sign the required approval and bankable concession agreement.
Actionable Strategies articulated benefits across several dimensions: Economic, Social, Environmental, Critical Infrastructure and Human Capacity. These aligned with UN Sustainable Development Goals and Myanmar’s Sustainable Development Plan. The project supported Myanmar’s commitment to the UN Paris Climate Accord.
 Actionable Strategies created the strategy and technology roadmap for the largest Smart Grid implementation in Turkey. Building on our technical assistance with distribution automation and AMI, the advanced Smart Grid integrated Microgrids, Distributed Generation, and Electric Vehicles. The strategy, architecture and technical approaches served as the model for other Smart Grids in the region. Technical challenges included integration of SAP IS/U via Enterprise Service Bus, deployment of a hybrid communications network, ingestion and analytics of real-time operational data, consolidated customer master data and cybersecurity.
Actionable Strategies created the strategy and technology roadmap for the largest Smart Grid implementation in Turkey. Building on our technical assistance with distribution automation and AMI, the advanced Smart Grid integrated Microgrids, Distributed Generation, and Electric Vehicles. The strategy, architecture and technical approaches served as the model for other Smart Grids in the region. Technical challenges included integration of SAP IS/U via Enterprise Service Bus, deployment of a hybrid communications network, ingestion and analytics of real-time operational data, consolidated customer master data and cybersecurity.

Actionable Strategies created the Enterprise Architecture for the Central Power Corporation of Vietnam. CPC is a state-owned power distribution utility that also operates some hydropower generators and EV charging infrastructure. CPC has a reputation in the Vietnamese energy sector for innovation.
Despite the success of individual applications, CPC was severely constrained in building enterprise applications as well as integrating new applications with existing software. Supporting a growing and transforming business was an increasing technology challenge.
Business drivers for the project included:
- Growing customer base
- Increased electricity demands
- Pressure to improve the reliability and quality of supply and service
Technical drivers included:
- Business process automation
- Lack of an enterprise architecture
- Need to incorporate power system operations and management functions
CPC’s stated objective was to develop an overall enterprise architecture, IT system infrastructure, and smart grid development strategy that includes an implementation plan that will improve operations and business processes. Targeted benefits included reduced system losses, improved management and operational efficiency, and improved quality of supply and electricity services to CPC customers.
Target State Architecture
The target state architecture applied the following core architectural principles.
- Integration via service bus: applications integrate with each other via the enterprise service bus
- Event-driven: applications publish relevant events on the bus in near real-time
- Common Information Model
- IEC CIM standards are applied to semantically consistent enterprise data
- CPC-specific information is conformed to a semantically consistent master data model and transactional data definitions
- Single source of truth: shared data is stored in the data warehouse
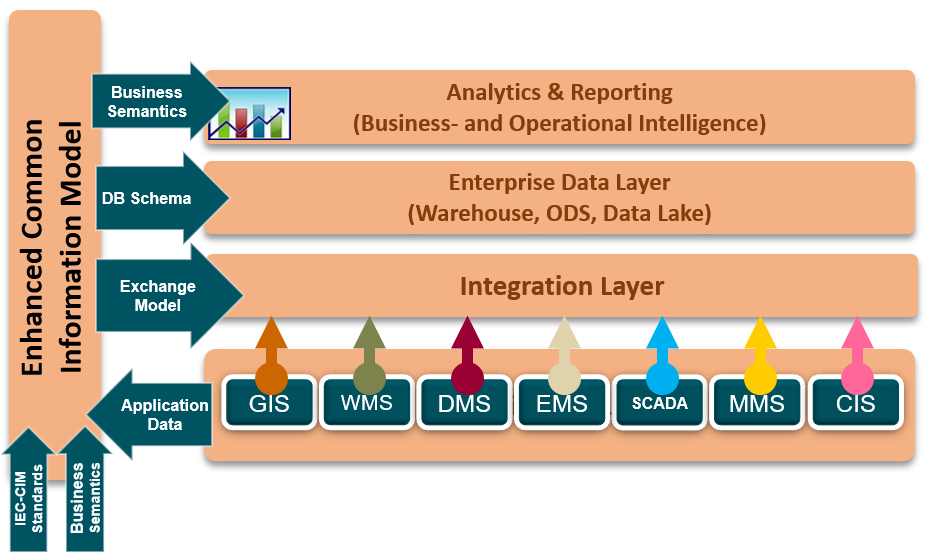
The to-be state of operational applications appears below. Back office applications would also use the Enterprise Service Bus and Data Warehouse.
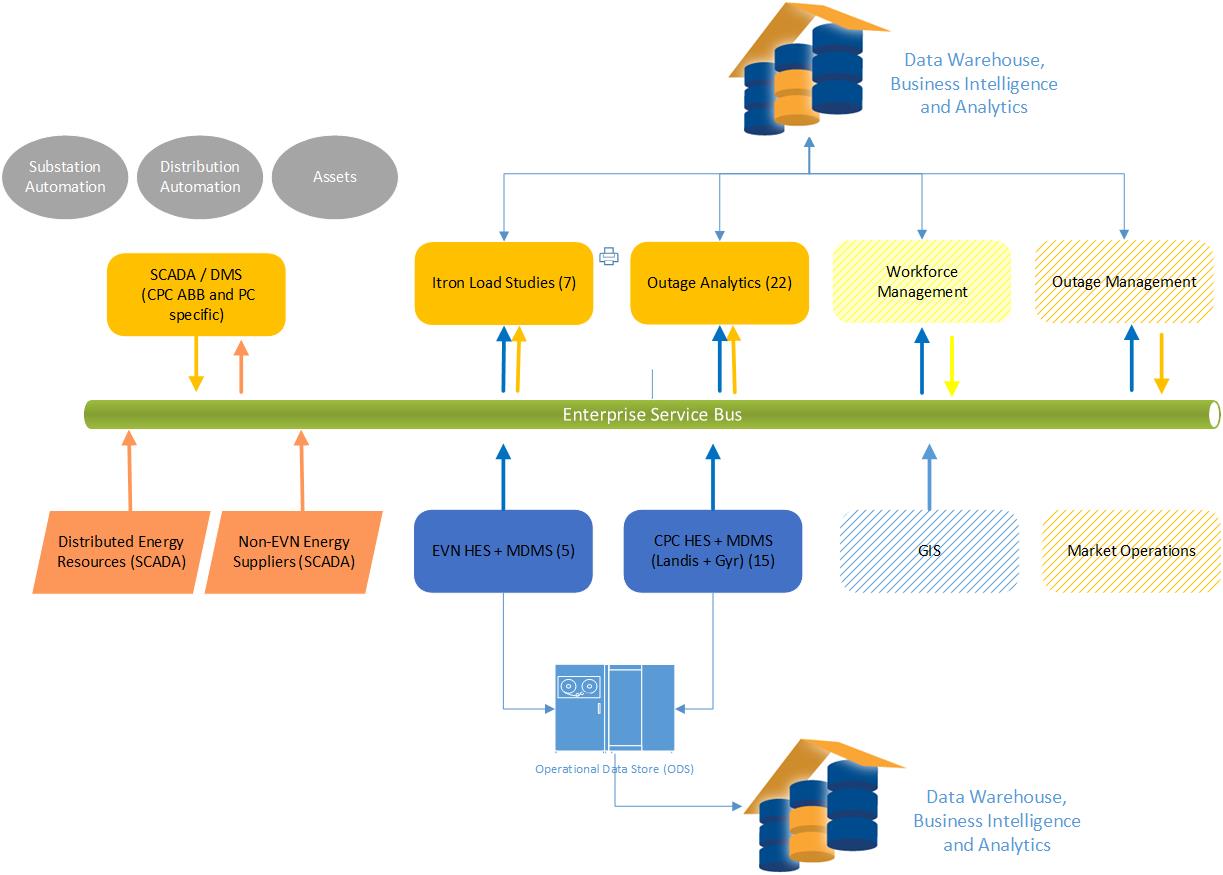
Enterprise Data Model
Actionable Strategies evaluated CPC’s proprietary data models and their integration with packaged platforms such as SAP/ISU. The enterprise data model provides:
- Consistent semantics which can be accelerated using the IEC Common Information Model which brings the ancillary benefit of the application of global standards
- Consolidation of data into a shared repository (data warehouse, ODS, data marts)
- Data governance and data quality management over enterprise data
- Geospatial data stored in a GIS
Loosely Coupled Applications
Applying a loosely coupled architecture provides many benefits to CPC in accelerating the delivery of applications and end-to-end solutions.
- Reduce development and maintenance
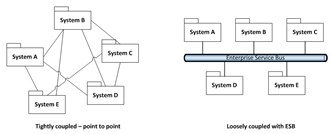 costs related to integration
costs related to integration - Integrate third party services readily
- Provide cost-efficient scalability
- Promote agility in development of integrated systems
- Enable resilience from a distributed architecture
The best practices of ESB and CIM have been proven in other markets and the benefits documented for CPC.
Retirement of Technical Debt
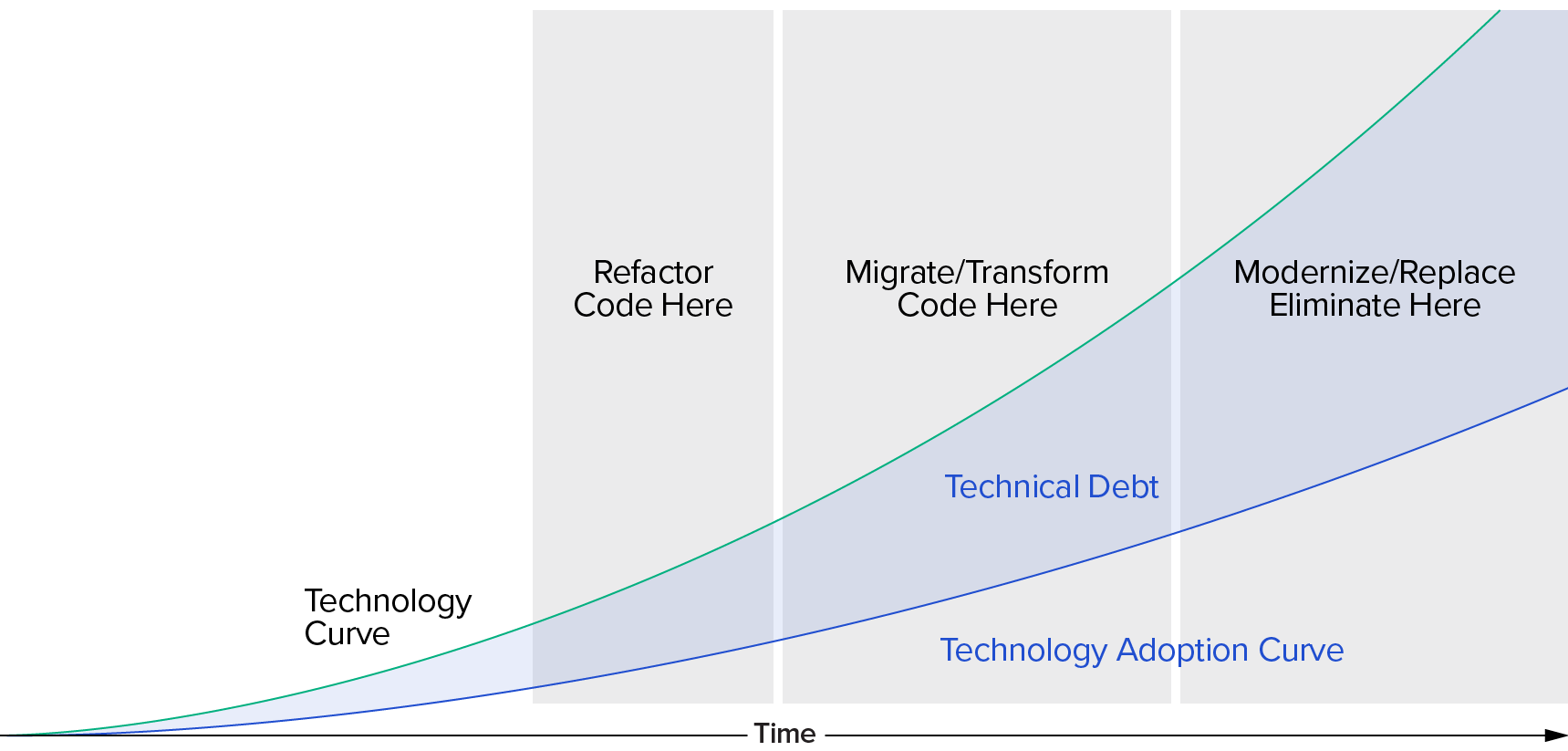 CPC has accumulated Technical Debt by building point (single purpose) applications to meet individual needs. While this provided value to a specific stakeholder, the ability for these applications to participate in an integrated portfolio servicing the CPC enterprise was diminished.
CPC has accumulated Technical Debt by building point (single purpose) applications to meet individual needs. While this provided value to a specific stakeholder, the ability for these applications to participate in an integrated portfolio servicing the CPC enterprise was diminished.
Technical debt increases as adoption rises which increases the number of integration points and data sharing requirements. These brittle interfaces drive up operating costs as the cost to enhance the applications also rise.
Retiring technical debt will mean that it no longer “crowds out” investment in new functionality. A technical model was provided to CPC to evaluate portfolio candidates and their disposition:
- Remain as-is
- Retire as no longer needed
- Rewire from point-to-point interfaces to ESB and the Data Warehouse (as a precursor to refactoring)
- Refactor under the Enterprise Architecture
- Rewrite using a CPC standard language, utilizing CPC tools and conforming to the EA
- Replace with a new or existing application
 A state-owned enterprise responsible for the distribution of electricity in Vietnam needed to design a compensation scheme for all levels of the organization. The introduction of market-oriented reforms includes competition for human capital. Compensation is now a critical part of recruiting, management and employee retention. Actionable Strategies was asked to design a measurement system for all of IT and then align a compensation model to it.
A state-owned enterprise responsible for the distribution of electricity in Vietnam needed to design a compensation scheme for all levels of the organization. The introduction of market-oriented reforms includes competition for human capital. Compensation is now a critical part of recruiting, management and employee retention. Actionable Strategies was asked to design a measurement system for all of IT and then align a compensation model to it.
An IT Balanced Scorecard was developed that aligned with the business Balanced Scorecard already is use. A tiered measurement system was designed that tied performance objectives to the strategic IT objectives. After investing the time in educating IT executives and front-line managers, Actionable Strategies let the now motivated leaders drive implementation.
 The City of Târgu Mureș in Transylvania aspired to become a Smart City and a model for Romania. Emerging markets are ideal candidates to leapfrog established markets through the application of advanced technologies.
The City of Târgu Mureș in Transylvania aspired to become a Smart City and a model for Romania. Emerging markets are ideal candidates to leapfrog established markets through the application of advanced technologies.
The Government of Romania set a “Digital Mures” Smart City agenda with two major objectives:
- Develop a modern infrastructure of private-public services
- Envision and develop a medical IT technology park specializing in research and medical information including telemedicine
The Smart City was expected to generate monetary savings, enhance the lifestyles of citizens and improve the private business environment. Incorporating experience from Telemedicine and Smart Grid projects in Romania, Actionable Strategies concluded that the technologies could support all of the strategic objectives.
Analysis of the structure, capabilities and preparedness of the city, we concluded that a number of constraints needed to be removed prior to implementing the strategic plan. The major issues were human capital, grid interoperability, the regulatory framework, culture, and real estate obstacles including buildings, property rights and energy data. The Government of Romania embraced our strategy and proceeded. By 2019, Romania had 330 Smart City projects covering over 6 million citizens.
 Bella Coola in British Columbia is home to the Nuxalk people, an indigenous First Nation of the Pacific Northwest Coast.
Bella Coola in British Columbia is home to the Nuxalk people, an indigenous First Nation of the Pacific Northwest Coast.
Due to its remote location, Bella Coola was not connected to BC Hydro’s provincial electricity grid. The community was powered by greenhouse gas-emitting diesel generators and by a run-of-river power facility. The hydro facility did not meet the full power needs of Bella Coola and had no storage capability.
The Hydrogen Assisted Renewable Power (HARP) project combined energy storage and hydrogen generation to reduce reliance on diesel power and incorporate additional clean power generation. The project lowered greenhouse gas emissions by 600 tons annually. Annual diesel consumption was reduced by over 52,000 gallons (200,000 liters) or $4.2 million at the time.
The Canadian government declared a number of social benefits which were delivered to a remote, indigenous population.
-
- Stimulating Canada’s green economy
- Creating jobs
- Helping protect the environment